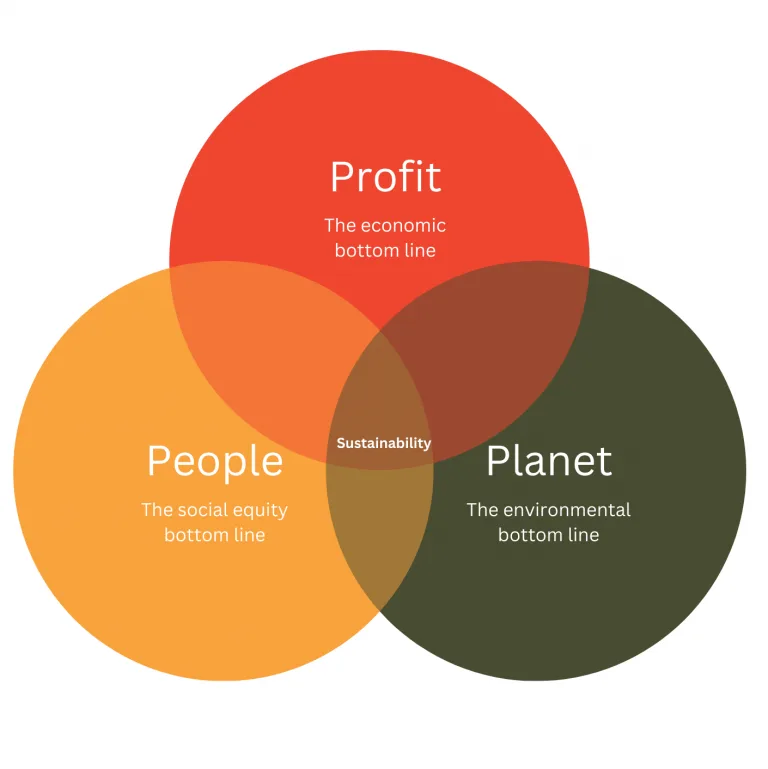
Eco-conscious consumers actively seek brands that align with their environmental and ethical values. For B2B companies, the growing demand for sustainability presents both a challenge and an opportunity to connect with consumers in authentic ways.
The concept of sustainable marketing refers to promoting products and services with an emphasis on social responsibility, environmental impact, and long-term value. We discussed sustainable marketing’s core principles, why it’s essential, and how brands can integrate it into their strategies to drive engagement, loyalty, and growth.
This article will explore:
- Increasing Demand for Sustainability in the Business Landscape
- Key Principles of Sustainable Marketing
- Understanding the New Eco-Conscious Consumer
- Building Authenticity in Sustainable Marketing
- Strategies for Implementing Sustainable Marketing in B2B
- Measuring the Impact of Sustainable Marketing Efforts
- Overcoming Challenges in Sustainable Marketing
Increasing Demand for Sustainability in the Business Landscape
Sustainable marketing is not just an ethical imperative; it’s a powerful tool for B2B companies to gain a competitive edge. Research by Nielsen shows that 66% of global consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable products, with that number climbing even higher among Millennials and Gen Z. B2B clients, increasingly influenced by end-consumer demand, now look for suppliers and partners who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
Incorporating sustainability into marketing can reshape a brand’s approach to better connect with eco-conscious consumers, foster long-term loyalty, and build brand trust.
Principle 1: Transparency and Honesty
- Building Trust through Transparency: Transparency is the foundation of sustainable marketing. Today’s consumers want clear information on product manufacturing, material sourcing, and environmental impact management. This open communication fosters trust, enhancing a brand’s appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
- Avoiding Greenwashing: Greenwashing—making misleading sustainability claims—erodes trust. Businesses that misrepresent their green practices face backlash from informed consumers and possible regulatory penalties. Transparent communication about materials, sourcing, production, and environmental impact is crucial.
Principle 2: Long-Term Value Creation
- Focus on Lasting Impact: Sustainable marketing focuses on long-term societal and environmental impact rather than short-term gains. Companies prioritising lasting change are more likely to build enduring consumer relationships. Instead of seeking immediate returns, sustainable marketing invests in initiatives with future benefits, like carbon reduction, resource efficiency, and community support.
- Brand Loyalty and Consumer Trust: Consumers appreciate brands with a genuine, long-term commitment to sustainability. When a company openly shares its environmental efforts, it builds credibility and fosters trust, aligning with clients’ values. Over time, as the brand consistently upholds its commitment to positive environmental and social impact, clients develop loyalty, feeling a shared resonance in values.
Principle 3: Environmental Responsibility
- Reducing Environmental Footprint: Environmental responsibility is central to sustainable marketing, with consumers expecting brands to reduce their ecological impact. Strategies include eco-friendly packaging, carbon neutrality, and responsible sourcing. By focusing on practices that minimise harm, brands show commitment to sustainability, enhancing their credibility and appeal to eco-conscious clients.
- Promoting Sustainable Consumption: Sustainable marketing goes beyond products to promote mindful consumption. Brands can influence responsible use, recycling, and proper disposal, fostering a sustainable product lifecycle. This approach positions the brand as a partner in consumers’ sustainability journey.
- Educational Campaigns: Education empowers consumers to make sustainable choices. By launching informative campaigns, brands boost credibility and deepen loyalty. Through resources like blogs, videos, and interactive tools, companies help consumers understand the environmental benefits of their products and adopt greener lifestyles, reinforcing their commitment to sustainability.
Principle 4: Consumer-Centric Innovation
- Developing Sustainable Products and Services: Creating products that meet consumer needs while being eco-friendly is crucial for sustainable marketing. This includes using sustainable materials, reducing emissions during production, and prioritising energy efficiency. By focusing on sustainable product development, brands can meet consumer demands and contribute to environmental preservation.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Embracing circular economy practices—recycling, refurbishing, and reusing—aligns with consumers’ preference for sustainable consumption. These efforts extend resource use, reduce waste, and conserve natural resources. Circular strategies support environmental goals, drive innovation in product design, and boost customer loyalty and brand reputation.
Principle 5: Social Responsibility and Community Engagement
- Prioritising Social Impact: Social responsibility is a key component of sustainable marketing that goes beyond environmental initiatives. It encompasses ethical considerations such as fair labour practices, responsible material sourcing, and community engagement. By prioritising these social dimensions, brands can show their commitment to making a positive societal impact, resonating with consumers who value ethical business practices.
- Supporting Local Communities: Investing in local communities enhances a brand’s reputation and fosters deeper relationships with consumers. By engaging in and supporting local initiatives—through sponsorship, partnerships, or direct investment—brands demonstrate their care for the social fabric of the areas they serve. This commitment to community well-being can boost consumer loyalty and trust, as customers take pride in supporting a brand that contributes to their local environment.
- Authentic Storytelling: Authentic storytelling is a powerful way for brands to create emotional connections with consumers. By sharing genuine stories and real outcomes from their social and environmental initiatives, brands can effectively convey their values and mission. This narrative approach enhances transparency and helps consumers recognise the tangible impact of the brand’s efforts. When consumers relate to a brand’s story and see the positive change it fosters, they are more likely to develop loyalty and advocacy, reinforcing the brand’s image as a responsible and caring organisation.
Principle 6: Measurement and Accountability
- Setting Measurable Goals: Defining measurable sustainability goals is crucial to ensure accountability. Goals like carbon reduction, water conservation, and waste minimisation should be specific and trackable, enabling companies to demonstrate progress. Setting and achieving these goals enhances credibility and builds trust with consumers.
- Transparency in Reporting: Brands can use annual or sustainability reports to demonstrate transparency and accountability. These reports should include both successes and areas for improvement, helping consumers understand the brand’s journey and ongoing commitment to sustainability.
- Using Consumer Feedback: Incorporating consumer feedback into sustainability strategies helps refine and improve sustainable practices. Regular surveys and feedback channels can provide valuable insights into consumer preferences and perceptions, enabling brands to make informed adjustments.
Understanding the New Eco-Conscious Consumer
Consumer Expectations
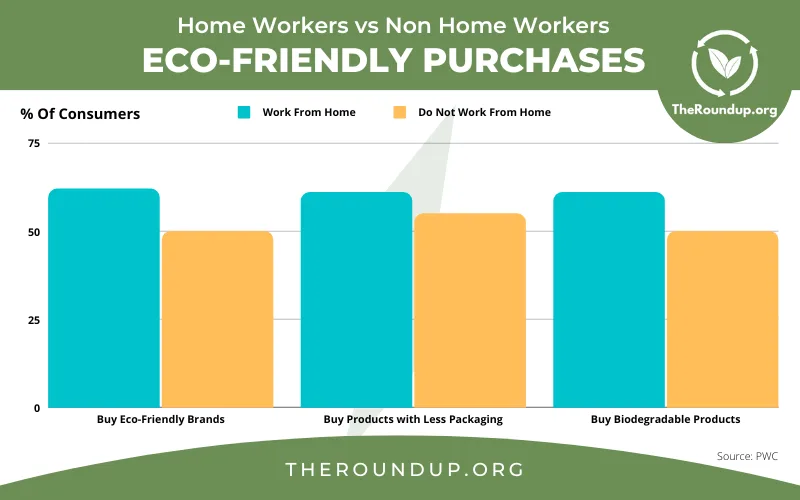
The eco-conscious consumer prioritises sustainable, ethical, and transparent brands. Recent statistics reveal that 81% of consumers feel strongly that companies should do more to address environmental issues. This trend drives demand for B2B clients, who now seek partnerships with brands sharing similar values.
Ethical and Environmental Impact
Today’s consumers care deeply about a brand’s environmental and ethical impact, and they scrutinise practices such as sourcing, production, and labour conditions. B2B clients also want assurance that their partners uphold similar values, ensuring their own reputations align with consumer expectations.
Long-Term Brand Loyalty
Companies that adopt transparent, genuine sustainability initiatives foster long-term loyalty. Consumers are more likely to stay with a brand that aligns with their values, building a foundation of trust and support.
Source: The Roundup Org
Building Authenticity in Sustainable Marketing
Transparency in Marketing
Honesty in sustainable messaging is critical. Consumers can detect greenwashing, and brands must be transparent about both successes and setbacks. For instance, Innocent Drinks maintains transparency by clearly communicating the environmental impact of its packaging, resonating with its eco-conscious consumer base.
Consistency Across Channels
Consistency in messaging is vital to establish credibility. B2B brands can reinforce their commitment to sustainability by maintaining uniform messages across all platforms, from websites to social media and advertisements. Consistent messaging reassures consumers of a brand’s dedication to sustainable values.
Case Studies
Brands like Seventh Generation, known for its commitment to eco-friendly cleaning products, successfully embody authentic messaging. Their marketing focuses on transparency and environmental stewardship, building a loyal customer base through a genuine commitment to sustainability.
Strategies for Implementing Sustainable Marketing in B2B
For B2B companies, implementing sustainable marketing is an essential strategy to align with the values of eco-conscious clients, showcase a commitment to environmental responsibility, and foster lasting client relationships.
These strategies offer actionable ways for B2B brands to effectively integrate sustainability into their marketing efforts.
Green Product Innovation
Green product innovation is at the forefront of sustainable marketing. Developing products or services with reduced environmental impact, using renewable resources, or improving energy efficiency can position a brand as a leader in sustainability.
For instance, tech companies can create energy-efficient data centres or design software optimised to minimise power consumption. In manufacturing, companies can focus on using recyclable materials, adopting biodegradable packaging, or designing products that are easier to repair or recycle, which appeals to eco-conscious clients prioritising sustainability in their procurement processes.
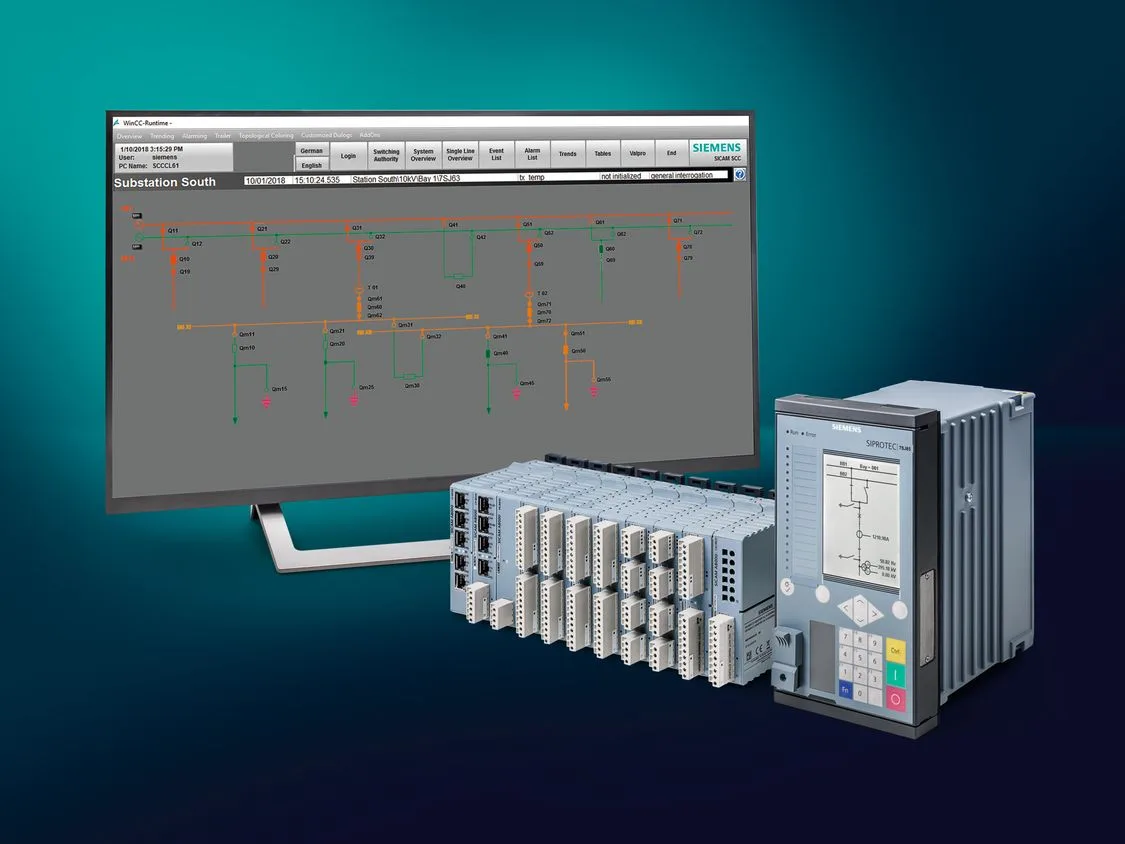
Source: Siemens
Case study: Siemens introduced an energy-efficient industrial automation system that consumes 30% less energy than its predecessors, helping clients reduce both costs and emissions. By aligning product development with sustainability goals, Siemens enhances its appeal to clients seeking greener solutions, showcasing the broader business and environmental benefits of their products.
Content Marketing on Sustainability
Educational content can be a powerful tool for promoting sustainable practices, demonstrating expertise, and reinforcing a brand’s commitment to eco-friendly values. By creating blogs, whitepapers, webinars, and infographics focused on sustainable practices, companies can help clients understand the importance and benefits of these approaches.
Such content can include practical guides on reducing waste, case studies on successful sustainability efforts, or reports on industry best practices, positioning the brand as a thought leader in sustainability.
Source: Schneider Electric
Case study: Schneider Electric regularly publishes content about energy efficiency, sustainable building practices, and resource conservation, aiming to inform clients and industry stakeholders about the latest trends and best practices. This type of content not only enhances Schneider Electric’s authority but also fosters stronger relationships with clients who value sustainability.
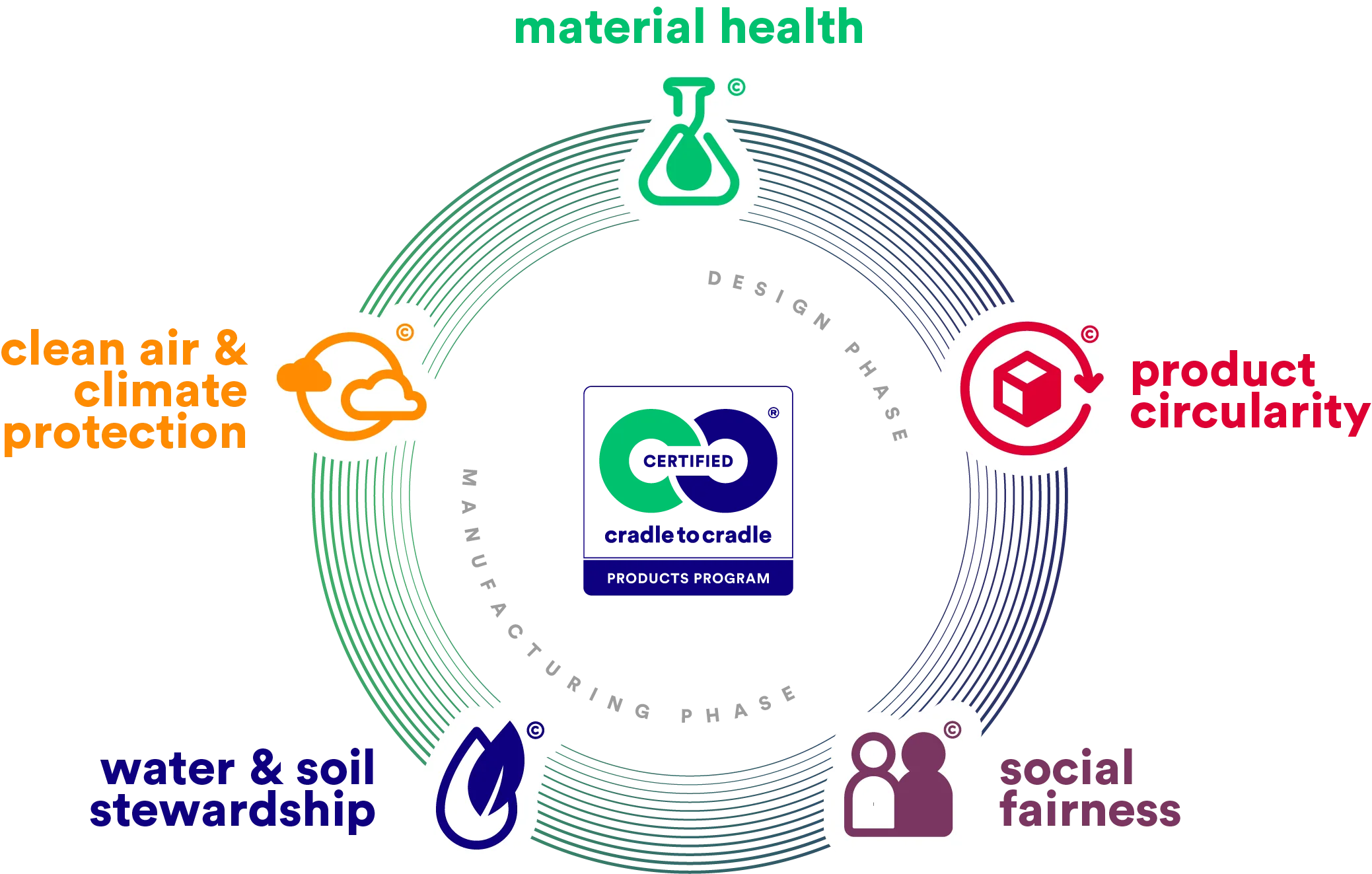
Leveraging Certifications and Partnerships
Certifications and partnerships are essential in enhancing a company’s credibility regarding its sustainability claims, serving as crucial factors for B2B clients when evaluating potential suppliers. Recognised eco-certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), Malaysian Green Label Certification, or international standards like B Corp and Fair Trade signal a verified commitment to sustainable and ethical practices.
Partnerships with organisations dedicated to sustainability can significantly expand a company’s reach and reinforce trust. In Malaysia, collaborations with local entities such as the Malaysian Sustainable Palm Oil (MSPO) certification or the Malaysia Green Technology Corporation can demonstrate a commitment to sustainable development that aligns with national goals.
Globally, partnerships with recognised organisations like the Cradle to Cradle Products Innovation Institute or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enhance credibility by showcasing adherence to sustainable design principles and best practices in product lifecycle management.
Source: C2C Certified
Case study: Interface Inc., a global leader in modular flooring, has earned numerous sustainability certifications, including LEED. By actively promoting these credentials, Interface builds confidence among clients in industries like construction and architecture that require sustainable building materials and practices. This partnership-based approach strengthens Interface’s standing in sustainability-focused B2B markets.
Highlighting Supply Chain Practices
Sustainability in the supply chain is becoming increasingly significant as clients look for transparency and ethical sourcing. Companies can showcase their commitment to sustainability by detailing the environmental and social practices within their supply chain, such as reducing emissions in transportation, using sustainable materials, or implementing fair labour practices.
Source: AMATA
A transparent supply chain provides an additional marketing advantage, as clients prefer partners whose values align with their own, especially when operating in industries that require compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Case study: Unilever has implemented transparency in its supply chain by mapping its suppliers and publishing detailed reports on sourcing practices for ingredients like palm oil and cocoa. This approach not only reassures clients about Unilever’s commitment to sustainability but also differentiates the brand in a competitive marketplace where transparency is valued.
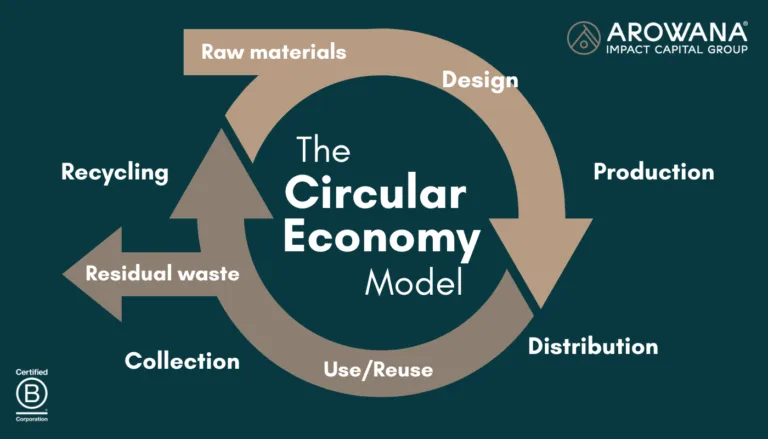
Embracing Circular Economy Practices
The circular economy, which focuses on reducing waste through recycling, reusing, and refurbishing, is gaining traction in sustainable marketing. B2B companies can adopt circular economy principles by creating take-back programmes, offering refurbished products, or designing products with reusable components.
Source: AROWANA
Not only does this approach extend the lifecycle of products, but it also minimises waste and showcases the brand’s commitment to sustainability. Circular economy practices align with the values of eco-conscious clients who aim to reduce their environmental footprint and are a compelling selling point in marketing materials.
Case study: HP has developed a programme that allows business clients to return their used cartridges for recycling. By focusing on the circular economy, HP reduces waste, supports resource efficiency, and helps clients meet their sustainability targets, enhancing its reputation as a leader in sustainable business solutions.
Data-Driven Sustainability Reporting
For B2B clients, quantitative proof of sustainability initiatives is essential. Data-driven sustainability reporting, which includes metrics on carbon emissions, water usage, waste reduction, and energy consumption, provides clients with measurable insights into a company’s environmental impact.
Source: International Accounting Bulletin
Regular sustainability reports and updates allow brands to demonstrate progress and accountability, which are essential for building client trust and demonstrating a genuine commitment to environmental goals.
This approach is particularly effective when the data shows tangible improvements, such as reduced carbon footprint or water savings, aligning with clients’ own sustainability goals.
Case study: 3M consistently publishes detailed sustainability reports outlining their progress on environmental goals, which include reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving product recyclability. This level of transparency not only builds trust with B2B clients but also serves as a powerful marketing tool that differentiates 3M as an industry leader in sustainable practices.
Measuring the Impact of Sustainable Marketing Efforts
As sustainable marketing is an evolving and multidimensional approach, brands need a clear framework to assess performance, refine strategies, and ensure their initiatives resonate with clients and stakeholders.
Defining Metrics
Traditional metrics such as customer engagement, brand perception, and loyalty growth offer a solid foundation, but sustainable marketing also requires targeted indicators that reflect the impact of eco-friendly efforts. Metrics may include:
- Customer Engagement on Sustainability Content: Tracking how clients interact with sustainability-focused content such as blog posts, whitepapers, or social media updates can reveal the level of interest and engagement with a brand’s sustainable initiatives. High engagement rates with sustainability content signal a strong client interest in these efforts.
- Brand Perception and Trust Levels: Surveys and sentiment analysis can gauge how clients perceive a brand’s commitment to sustainability. Improved brand perception around sustainable practices can translate to enhanced loyalty and positive word-of-mouth among B2B clients.
- Loyalty and Retention Rates: Tracking changes in client retention and loyalty among eco-conscious clients offers insight into the lasting impact of sustainable initiatives. Brands that consistently prioritise and demonstrate sustainability are likely to retain clients who value these principles.
- Environmental Impact Data: Quantitative metrics, such as reductions in carbon emissions or waste, provide tangible proof of a brand’s environmental initiatives. By sharing this data with clients, companies can reinforce their credibility and demonstrate measurable progress, which further strengthens trust.
Evaluating Consumer Feedback
Collecting and analysing consumer feedback on sustainability initiatives provides invaluable insights that can shape future marketing strategies. Tools for gathering feedback include:
- Surveys and Interviews: Regular surveys and in-depth interviews allow companies to capture clients’ views on their sustainable efforts, helping to identify areas where expectations are being met or where there may be gaps. This method provides qualitative data, enabling brands to understand the nuances of client expectations around sustainability.
- Analytics on Sustainable Product or Service Usage: Tracking the adoption and usage rates of sustainably designed products or services offers insights into client satisfaction and the actual impact of sustainable offerings. For instance, if a B2B software company offers an eco-friendly, energy-efficient solution, usage data can highlight whether clients are leveraging the product to meet their sustainability goals.
- Social Listening and Sentiment Analysis: Monitoring discussions on social media platforms and online forums for brand mentions related to sustainability can reveal how clients feel about a company’s green efforts. Positive sentiment can signal alignment with client values, while constructive criticism can inform areas for improvement.
Adjusting Strategies Based on Results
By evaluating the data gathered through metrics and feedback, companies can identify areas of success as well as opportunities for improvement. Adjusting strategies based on these insights helps companies maintain a strong alignment with client expectations and industry trends.
- Iterative Improvements: As brands receive feedback and performance data, they can make incremental improvements to their sustainable marketing strategies. For example, if clients express interest in more detailed information about the supply chain, companies can increase transparency by sharing additional data or implementing traceability technologies.
- Experimenting with New Initiatives: The evolving nature of sustainable marketing provides opportunities for companies to test innovative approaches. Based on insights gathered, brands can pilot new initiatives, such as expanding eco-friendly product lines or launching educational campaigns on sustainable practices, to gauge client response before full-scale implementation.
- Responding to Industry Trends: The sustainability landscape is dynamic, with new trends and regulatory requirements emerging regularly. Brands must stay agile and responsive to these changes by adjusting their strategies to remain relevant. For example, if there is a growing focus on carbon neutrality in the industry, a brand could emphasise carbon-reduction efforts in its marketing to align with client expectations.
Overcoming Challenges in Sustainable Marketing
Implementing sustainable marketing comes with unique challenges. Addressing these obstacles head-on is crucial for building a sustainable brand that resonates with eco-conscious clients and drives lasting success.
Balancing Profitability and Sustainability
Source: Inchainge
One of the main challenges in sustainable marketing is balancing sustainability goals with profitability. Sustainable initiatives often require upfront investments in eco-friendly materials, waste reduction processes, or energy-saving technologies, which can strain resources, especially for companies with tight margins. However, many businesses discover that these sustainable practices can support long-term profitability. Benefits include:
- Cost Savings from Operational Efficiency: Sustainable practices often lead to reductions in energy, waste, and resource consumption, which can translate to substantial cost savings. For example, switching to renewable energy sources, using recycled materials, or reducing packaging waste can decrease operational costs over time.
- Enhanced Brand Value and Customer Loyalty: As consumers increasingly seek out environmentally responsible companies, brands that prioritise sustainability can experience higher customer loyalty and willingness to pay a premium for green products. This boost in brand value can provide a competitive edge and support long-term financial performance.
- Access to New Revenue Streams: Sustainability can also open up opportunities to tap into new markets or develop innovative products and services that appeal to eco-conscious clients. For instance, technology companies that design energy-efficient solutions or recyclable hardware find an increasing demand among businesses committed to reducing their carbon footprint
Avoiding Greenwashing Pitfalls
Source: The Crisps
Greenwashing not only erodes consumer trust but can also attract regulatory scrutiny and harm a brand’s reputation. To avoid these pitfalls, companies should:
- Ensure Credible and Validated Claims: Brands must back all sustainability claims with verifiable data and avoid overstatements that could be misleading. If a company claims its product is “100% sustainable” without sufficient evidence, it risks undermining its credibility.
- Transparency in Communication: Clear, honest communication about sustainable practices, even when they are still in progress, resonates well with clients. Consumers appreciate when companies are upfront about their sustainability journey, including areas where improvements are still needed.
- Use Third-Party Certifications: Valid certifications like B Corp, Fair Trade, or LEED provide an extra layer of credibility to sustainability claims, ensuring clients that these practices meet recognised standards. By obtaining trusted certifications, companies can differentiate themselves and reassure eco-conscious consumers of their genuine commitment.
Internal Education and Commitment
Source: Science Direct
Building a sustainable company culture requires deep-rooted commitment and education across all organisational levels. Internal education ensures that employees at every level understand the brand’s sustainability goals and feel empowered to contribute to them. Key strategies include:
- Training and Awareness Programmes: Educating employees on sustainability concepts, from reducing waste to understanding eco-friendly production, can enhance commitment to sustainable goals. Training programmes help staff see how their roles align with broader environmental objectives and increase motivation to support these efforts.
- Incorporating Sustainability into Core Values: For a brand’s sustainability message to be truly authentic, it should be embedded in its mission and values. Regularly communicating the importance of these values fosters a culture where employees take pride in the brand’s sustainability journey.
- Empowering Employees to Participate: Encouraging employees to contribute to sustainable initiatives, such as creating greener product ideas or suggesting ways to reduce waste in daily operations, can reinforce a culture of environmental responsibility. When employees feel involved in sustainability efforts, they are more likely to advocate for the brand’s values, both within and outside the company.
Final Takeaways
Sustainable marketing offers B2B companies a unique opportunity to connect with eco-conscious consumers, build long-lasting relationships, and differentiate themselves in a competitive marketplace. By embedding sustainability into their core values, brands can meet the expectations of today’s socially conscious clients, paving the way for mutual growth and positive environmental impact.
In a rapidly evolving business landscape, sustainable marketing has become more than just a trend—it is a strategic approach for achieving brand success and building consumer trust in a changing world.