Creating a successful product isn’t just about having a good idea; it’s about turning that idea into something that users love and find useful. This is where the product design process comes in, helping companies systematically bring their ideas to life. In this article, we’ll explore the key stages of the product design process that can significantly boost your chances of success:
Understanding the Product Design Process
The product design process is a series of steps that take a product from concept to reality. This structured approach ensures that the finished product meets user needs, solves a problem, and stands out in the marketplace. Following a systematic process allows for thorough research, idea generation, refinement, and testing, helping to minimise risks and ensure the product resonates with the target audience.
Stages of the Product Design Process
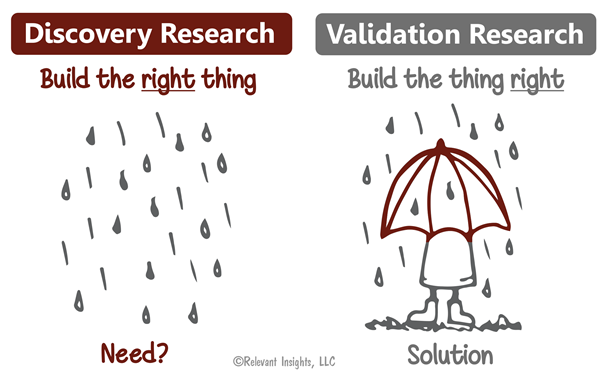
Stage 1: Research and Discovery
The first stage of the process is all about understanding. Before jumping into designing a product, it’s crucial to know who your users are and what problems they need solving. This is where research and discovery come into play. Conducting surveys and interviews with potential customers can offer insights into their pain points, while analysing competitors helps you spot gaps in the market. You can also conduct a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) to better understand the competitive landscape.
Best Practices:
- Use surveys and interviews to gather user feedback and identify problem-solving opportunities.
- Analyse competitors and conduct a SWOT analysis to understand market trends.
- Create user personas to visualise your target users and their needs.
Source: Relevant Insights
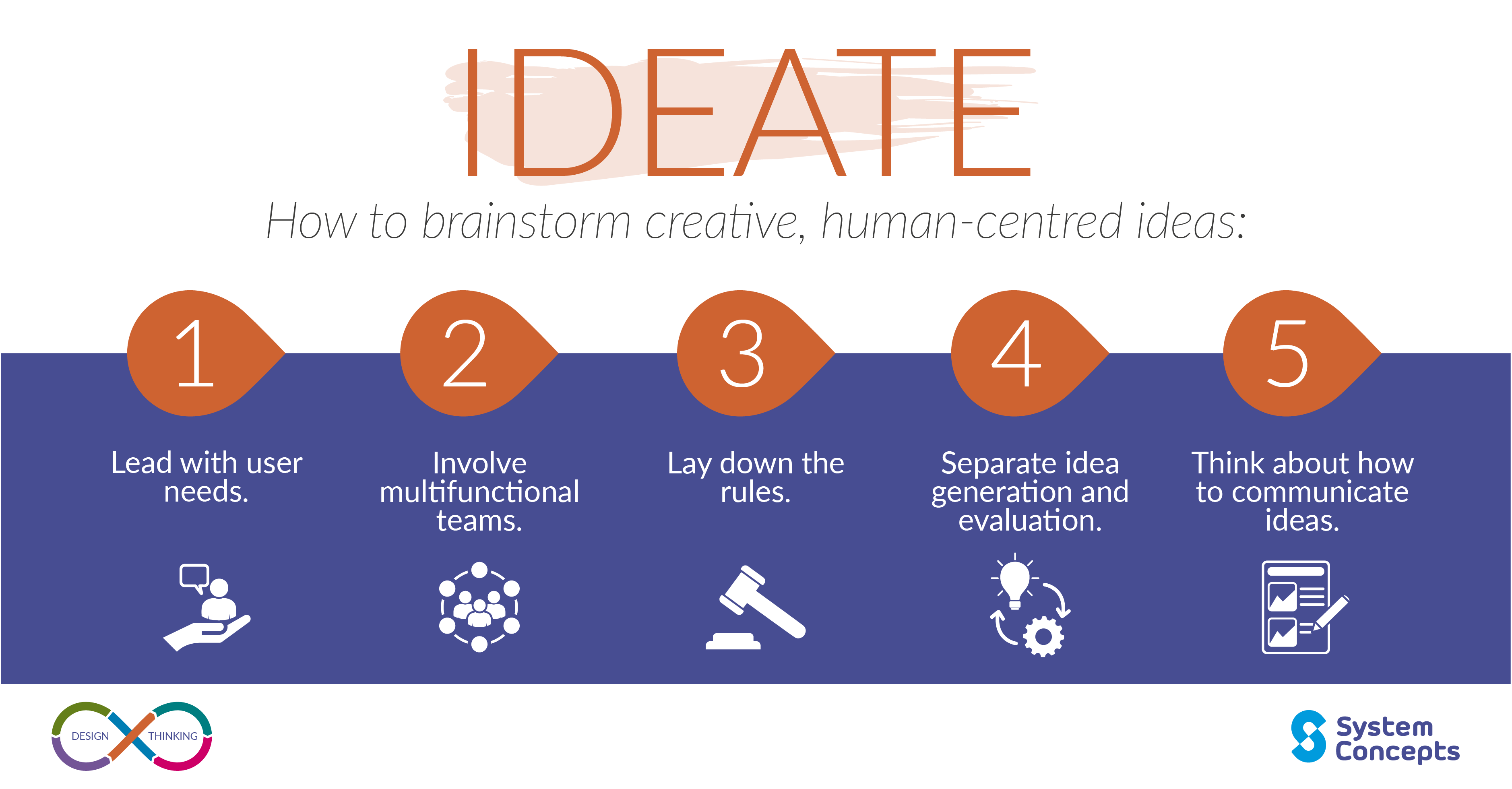
Stage 2: Ideation
Once you have a clear understanding of your users, the next step is ideation—this is where creativity takes centre stage. Ideation involves brainstorming, sketching, and coming up with as many product ideas as possible. The goal here is to explore a wide range of possibilities without worrying about whether or not they’re feasible at this point.
Best Practices:
- Use brainstorming sessions to generate a variety of ideas for solving user problems.
- Sketch your ideas to visualise concepts quickly.
- Employ design thinking techniques to focus on user interaction and solutions that cater to the needs of your target audience.
Source: System Concepts
Stage 3: Concept Development
After ideation, it’s time to take the best ideas and turn them into tangible concepts. This is where you create prototypes or mockups—low-fidelity versions of the product that can be used to gather feedback from real users. Concept development is about refining those initial ideas and testing them in the real world to see what works and what doesn’t. Collaborating with the product development team is crucial at this stage to ensure everyone is aligned.
Best Practices:
- Develop prototypes or mockups to make product ideas tangible.
- Gather feedback from real users early to avoid costly mistakes later.
- Refine your concepts based on this feedback and involve your team members in the process.
Source: Slickplan
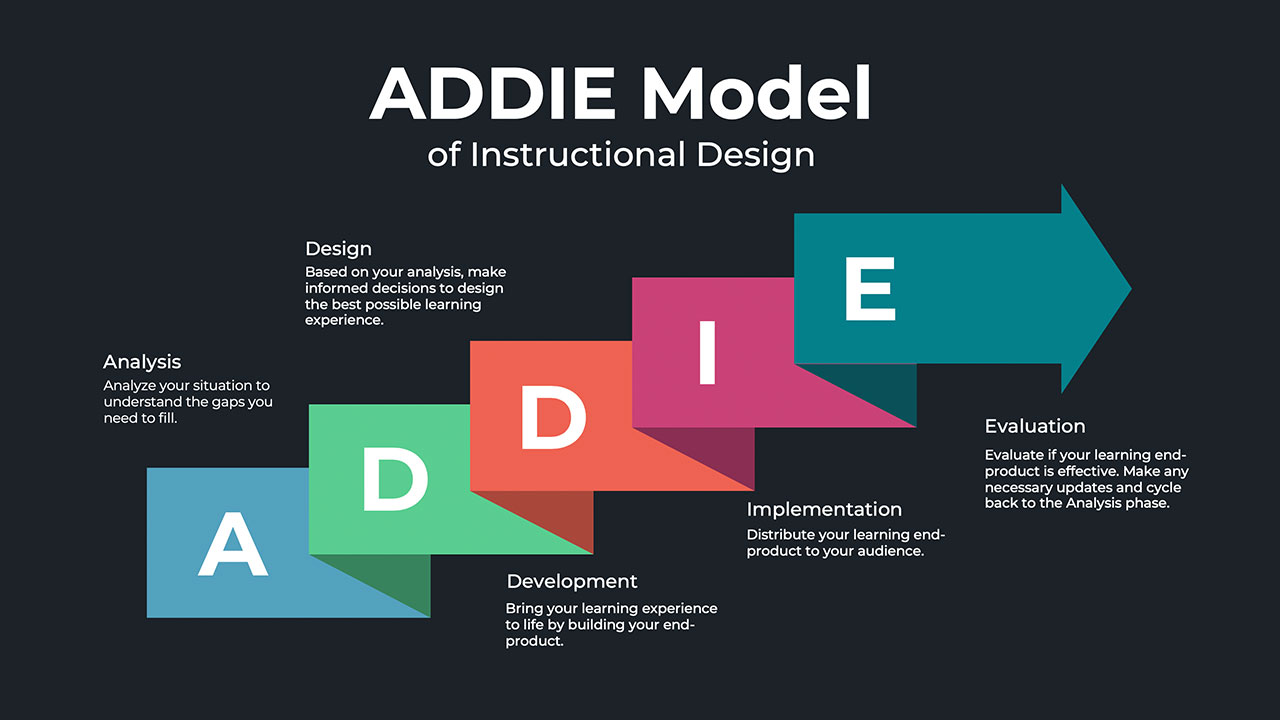
Stage 4: Design Development
With a solid concept in place, the design development phase focuses on fleshing out the details. This is where cross-functional collaboration becomes crucial, as designers work closely with engineers, marketers, and other stakeholders to ensure that the final product is not only visually appealing but also practical to manufacture. Collaboration between designers and developers ensures that both technical and aesthetic aspects are aligned.
Best Practices:
- Work with cross-functional teams, including the product development team, to ensure design feasibility.
- Consider the manufacturing process to avoid design complications.
- Maintain open communication between UX designers, developers, and other stakeholders.
Source: Water Bear Learning
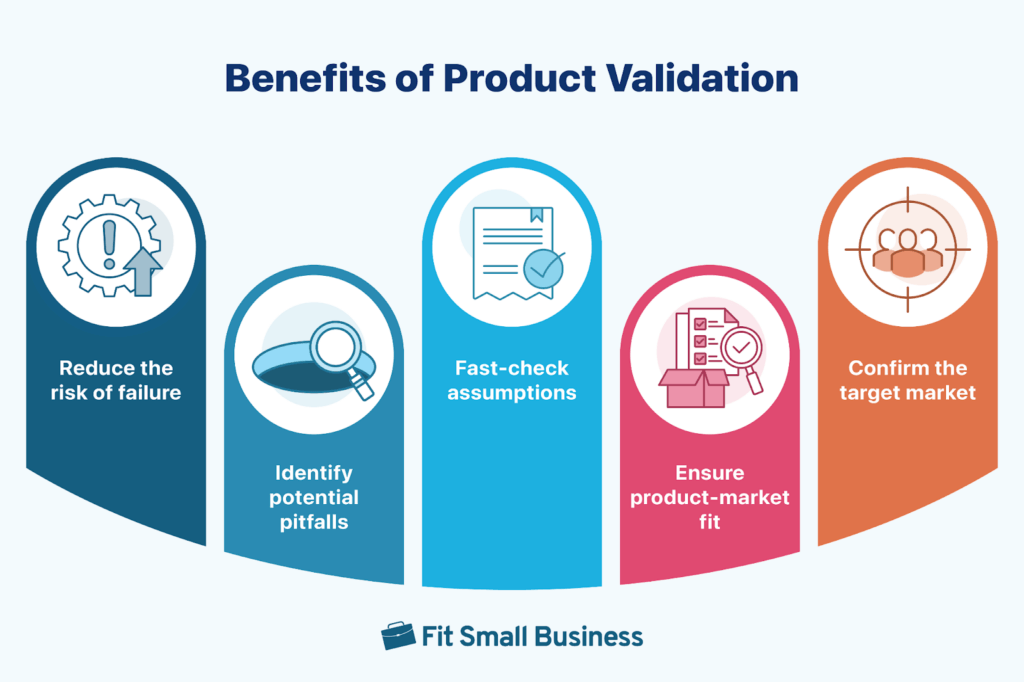
Stage 5: Testing and Validation
Once the design is finalised, it’s time to test it out. Testing and validation ensure that the product is both usable and functional in real-world conditions. This might involve conducting user experience (UX) testing sessions where participants try out the product and provide feedback, or A/B testing to see which version performs better. The goal is to identify and fix any issues before the product hits the market.
Best Practices:
- Use user testing to assess the product’s usability and functionality.
- Conduct A/B testing to compare different versions of the product.
- Continuously gather feedback from target users to refine the product.
Source: Fit Smal Business
Stage 6: Launch
After rigorous testing, the product is finally ready to be launched. But a successful launch isn’t just about putting the product on the market—it also involves developing a solid marketing strategy. This includes establishing sales channels, promoting the product, and ensuring that your business goals are aligned with your marketing efforts. Ensuring that the product launch reaches the right target audience is key to maximising its impact.
Best Practices:
- Create a detailed launch plan, including marketing and sales strategies aligned with business goals.
- Promote the product across relevant channels to reach your target audience.
- Monitor the initial performance to make adjustments if necessary.
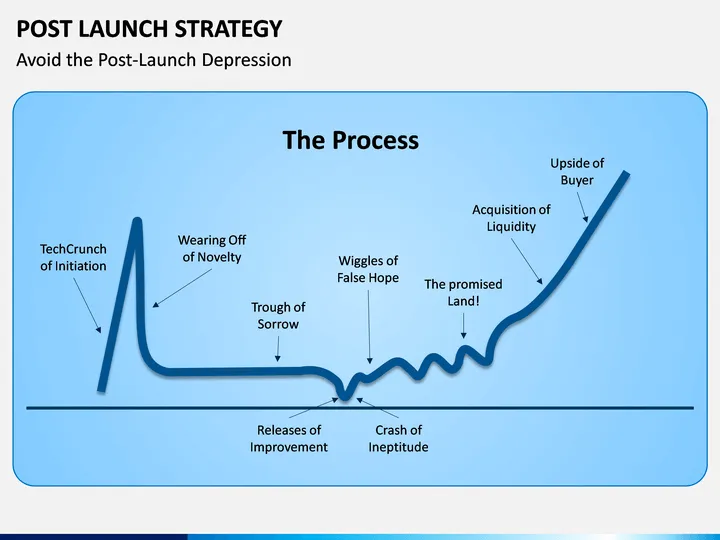
Stage 7: Post-Launch Evaluation
The product design process doesn’t end at launch. In fact, post-launch evaluation is crucial to understanding how users are interacting with the product in real-life scenarios. By gathering data on user experience (UX) and sales performance, companies can make necessary improvements, ensuring the product continues to meet evolving user needs.
- Understanding User Experience: Real-world use often uncovers issues that weren’t visible during testing. Collecting feedback helps identify usability problems, allowing for timely adjustments.
- Continuous Improvement: Product design is an iterative process. Continuous evaluation enables companies to refine and update their products based on user interaction and market demands.
- Measuring Success: Defining clear metrics like user satisfaction, market share, and revenue allows businesses to track their product’s performance and plan future strategies.
Source: Weave Media Team
Best Practices:
- Tracking User Engagement: Platforms like Google Analytics can track how users interact with your product. Key metrics like daily active users (DAUs) and feature usage offer insights into what’s working and what needs improvement.
- Sales Data Analysis: Analysing sales performance is vital in measuring the product’s financial success. Metrics such as total sales and conversion rates provide a clear picture of how well the final product is performing in the market.
- Conducting Post-Launch Surveys: Gathering direct feedback from users through surveys helps identify areas for improvement. Surveys like Net Promoter Score (NPS) or customer satisfaction surveys provide valuable insights into how users feel about the product.
- Analysing Feedback: The data collected from user experience (UX), sales, and surveys should be compiled and analysed to identify patterns. Spotting recurring issues or trends helps inform future product updates or new feature developments.
Actionable Steps for Improvement:
- Iterative Design: Use the feedback you’ve gathered to make informed decisions about product updates or future versions. This continuous loop of feedback and improvement ensures that your product remains relevant.
- Prioritising Changes: Not every piece of feedback will be equally important. Prioritise changes based on user impact, feasibility, and alignment with your business goals.
Final Takeaways
Mastering the product design process is about more than just following a set of steps—it’s about continually refining and improving your approach to meet user needs and market demands. By understanding each stage of the product design, from research and ideation to post-launch evaluation, you can develop products that not only succeed in the marketplace but also provide lasting value to your users.
No matter the scale of your project, applying these best practices can help you bring innovative ideas to life and set your product up for success.